HISTORY:

Sir Isaac Newton was an English mathematician, physicist, and astronaut. He is considered the founder of the classical mechanic.
Some of his work was focusing on finding the nature of the white light, and the law of gravitation.
In this book:
Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica was published in 1687. He wrote 3 main laws of motion:
-
-
- First Law:
A body at rest will remain at rest, and a body in motion will remain in motion unless it is compelled to change its state by forces acting on it.
-
- Second Law:
The sum of forces, F acting on a body is equal to its mass, m, times its acceleration.
-
- ∑F = ma
-
-
- Third Law:
To every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
-
LAW EXPLANATION:
First Law:A body at rest will remain at rest, and a body in motion will remain in motion unless it is compelled to change its state by forces acting on it. Explanation:
|
The mathematical explanation is: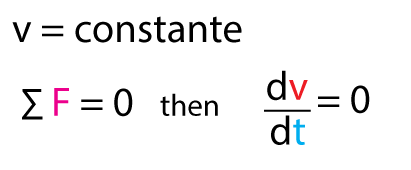 |
